How Credit Score Ranges Matter

A high credit score means you’re a low-risk borrower, which could lead to lower interest rates on loans and other lines of credit. On the other hand, low credit scores could mean higher interest rates and a greater chance of not being approved for a loan.
While most people know they have credit scores, they may not understand why these score numbers matter or how they are determined. Read on as we explore how different credit score ranges map to financial situations and tips on how you can improve your credit score.
What Credit Score Ranges Should Mean To You
Different credit score ranges correspond to varying levels of risk. Knowing your credit score is incredibly helpful when it comes to determining whether you will qualify for a loan or credit card.
Credit card companies and lenders use credit scores to determine your loan qualification, credit limit, and applicable interest rate. Lenders often give more appealing interest rates to people with high credit scores because there is a lower chance of the debt not being repaid by the borrower.
Since people with low credit scores are considered high-risk borrowers, they may have trouble getting approved for various financial products, including personal and credit cards. As a result, they could be charged higher interest rates or denied credit entirely.
What Are the Credit Score Ranges?
Credit scoring companies like FICO use multiple credit scoring models to determine your credit score. FICO scores dominate the market, and the most popular versions range from 300-850, with each number indicating how likely you are to be a responsible borrower. Below are the different credit score ranges and what they represent financially:
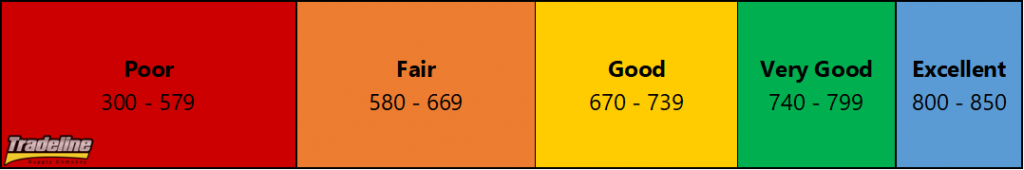
Commonly used FICO credit scores range from 300 to 850.
Exceptional 800-850
Consumers with exceptional credit scores have consistently excellent credit usage behavior. They have low balances on their credit card accounts, maintain their credit utilization ratios around 10% or lower, and have a long history (decades) of on-time monthly payments. Borrowers within this range are offered higher credit limits and can qualify for lower rates on personal loans, credit cards, lines of credit, and mortgages.
The highest possible credit score you can have on the FICO scoring system is 850. While it is possible to obtain a perfect 850 credit score, it is not necessary to do so in order to get the best credit offers, nor is it a practical goal. Getting an 850 credit score requires that every single credit scoring factor must be perfect, which is simply not possible for most consumers.
Consumers with credit score ranges that are very good or exceptional will get the best interest rates on mortgages and other loans.
Very Good 740-799
A score between 740 and 799 is in the very good credit range. These borrowers generally have good financial responsibility regarding credit and money management. They have lower credit utilization ratios, a good history of on-time payments, and few derogatory marks on their credit reports.
Most lenders are still comfortable extending lines of credit to these borrowers, so people within this range are likely to get approved for loans and other products with favorable interest rates.
Good 670-739
A FICO score falling between 670 and 739 is considered a good credit score. The national average credit score stands in this range. This score indicates that you have generally been responsible with credit in the past and paid your bills on time. You may qualify for average rates, but it may become more difficult to be approved for some types of credit. You’ll likely have to shop around in order to find the best interest rates.
Fair 580-669
Individuals with credit scores within this range are below the national average and may have negative marks on their credit reports. If you have a FICO score in this range, you’ve likely missed payments or shown signs of high credit usage and delinquencies. This means you may not qualify for some types of credit, such as loans or credit cards. Few lenders will likely extend a credit line to you but offer high-interest rates.
Poor 300-580
This range is the lowest credit score rating on credit reports and is considered to be very bad credit. People with a FICO score in this range are seen as high-risk borrowers and may be unable to get approved for loans, lines of credit, or mortgages. They have several cases of missed payments, high balances, and high credit utilization ratios. Poor credit scores may also result from filing bankruptcy or having debt in collections.
“Credit invisibles” are those who do not have a credit score, which can be equally as problematic as having bad credit.
No Credit Score
It is possible to not have a credit score at all, which is known as being credit invisible. If you haven’t had a loan or credit card for several years, your credit score may not be able to be calculated because there is insufficient information on your credit reports.
Lenders may still allow you access to credit based on your other assets, but it usually requires additional verification of your assets and income.
How To Build Credit & Earn A Better Credit Score
Building and improving your credit score can be a challenging but rewarding experience. Your credit score will increase your access to financing products with lower interest rates and fees on everything from loans to mortgages. Below are some tips that can help improve your score:
Make all of your monthly payments on time – One of the most significant factors that go into calculating your credit score is your payment history. A history of on-time payments will help boost your credit score. If you miss payments, this can be reported to credit reporting agencies and damage your credit score.
Pay more than the minimum payment – By only making the minimum payment each month, you make it easier for yourself to accumulate more and more debt. Not paying your balance in full also increases your utilization ratio, which impacts your score negatively the higher your utilization becomes. Focus on paying off as much of the balance as possible each month.
Keep credit card balances low – Again, carrying large balances negatively impacts your credit score, so it is important to consistently keep your balances low if you can. If you have large outstanding credit card balances on your accounts compared to your available credit, lenders are also more reluctant to give you a new line of credit because they may view you as financially over-extended.
Keeping your credit cards open while maintaining low balances helps your credit utilization and, by extension, your credit score.
Keep your credit cards open – Closing a credit card account can hurt your credit score because you no longer get the benefit of its credit limit. Keeping your credit cards open even if you are not using them much allows the cards to help out your credit utilization metrics, boosting your credit scores.
Only apply for credit when you need it – Each time you apply for a new loan or credit card, lenders check your credit report, which results in a hard inquiry being added to your credit report. Having too many hard inquiries within the past year can impact your score negatively. If lenders see a lot of inquiries in your credit history, they may be concerned that you are taking on too much new debt and might not be able to make all of your payments on time.
Why You Should Never Trust a CPN to Boost a Credit Score Range
If you’re looking to boost or reset your credit score and come across a company that offers Credit Privacy Numbers (CPN), it’s best to stay away. A CPN is a nine-digit fake or stolen Social Security number that credit repair companies sell to people who want to repair their credit scores.
These companies instruct you to use the CPN in place of your Social Security Number when applying for credit. CPNs are generated randomly or stolen Social Security numbers, mostly from children, inmates, and senior citizens. Using a CPN is illegal, and when caught, you can face a hefty fine or even jail time.
Using a CPN instead of a stolen Social Security number, you may be committing an identity theft crime. Depending on your state and the statute of limitations, you could be jailed for a maximum of 15 years and face thousands in fines. Using a CPN to reset or boost your credit score is not worth the risk.
7 Fast Credit Building Strategies to Influence Your Credit Score Range
Credit scores have become an essential part of today’s society. It’s no longer just used for loan applications. Employers and landlords may also ask to review your credit score or credit history. In some cases, you may not get access to housing, utilities, or insurance if you have a low credit score.
If your credit score isn’t your ideal number, or is below the average credit score, there are several things you can do to help increase it. Here are seven fast strategies to help improve your credit score range:
1. Develop Your Credit File
Creating a positive credit file is the first step in building credit. This can be done by opening a credit line that is reported to the major credit bureaus. If you make on-time monthly payments and keep your revolving utilization ratio below 30%, this demonstration of good credit behavior will increase your credit score and, in turn, boost your credit score range. Higher credit scores will open doors to better financing options and lower rates.
2. Check Your Credit Reports
When building your credit score range, it’s critical to check your credit reports to know where you stand.
As mandated by the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), you can get your credit report for free once a year from each of the three credit bureaus. Additionally, during the COVID pandemic, the credit bureaus have volunteered to provide free credit reports to everyone on a weekly basis. This
Review each credit report for inaccurate information and dispute errors as necessary.
3. Dispute Credit Report Errors
Your credit score can be significantly lowered if your credit report contains erroneous negative items. However, the credit bureaus can be contacted if any errors are found. Your dispute letter must be investigated and responded to by the credit bureau within 30 days. If you find the information to be inaccurate, you can request that it be removed or corrected on your credit report.
4. Pay Your Bills on Time
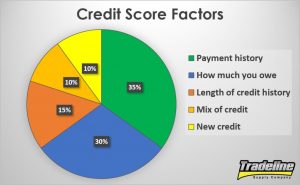
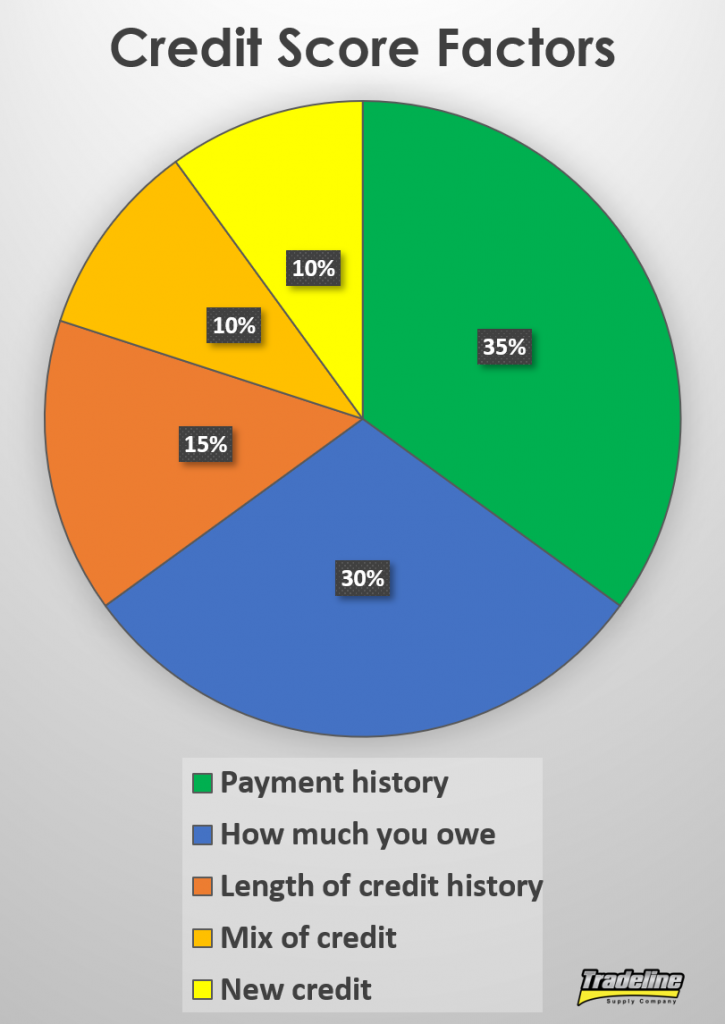
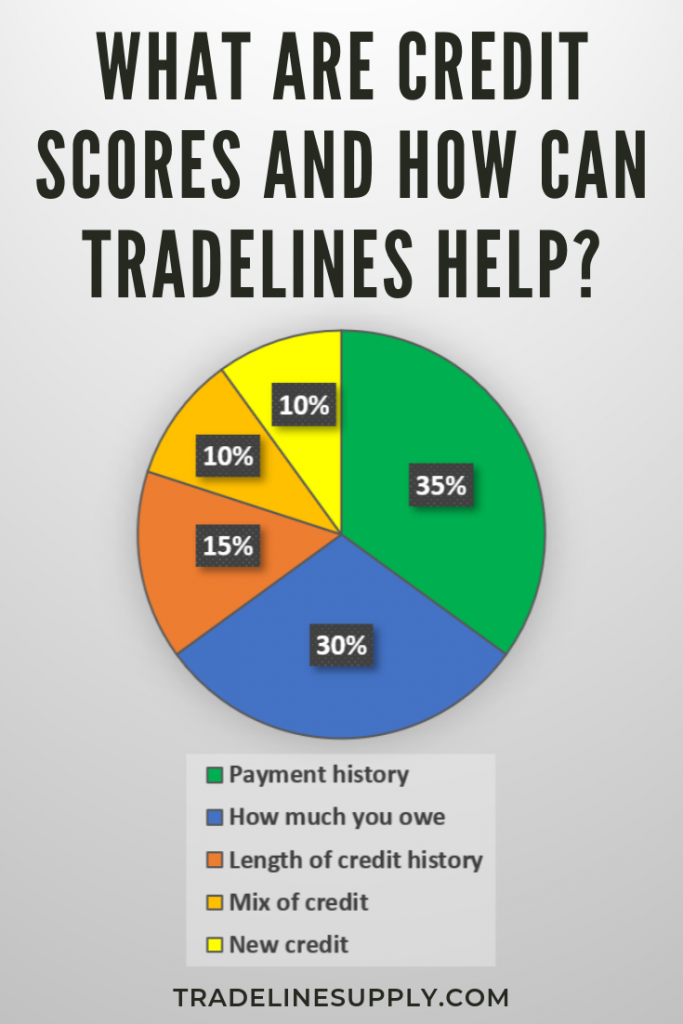
Payment history is the most critical factor in your credit score, accounting for 35% of your score. No credit-building strategy will be effective if you do not consistently pay your bills on time. Late payments can remain on your credit report for up to seven years.
If you do this successfully, having a long history of on-time bill payments will help you achieve excellent credit scores. To avoid accidental missing or late payments, you can set up reminder notifications and automatic bill payments with your lenders.
5. Increase Your Credit Limit
Paying off credit cards and other revolving accounts may help boost your credit score range, but having a high amount of available credit will add points to your score. Consider increasing the limit on your lines of credit to decrease your utilization ratio. An ideal time to do this is after building up a history of responsible credit usage or when you have started a better-paying job.
According to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, your payment history, credit mix, debt owed, and length of your credit history are some important credit factors a credit card issuer will look at when determining your credit limits.
6. Catch Up on Delinquencies and Past Due Accounts
If you have missed payments in the past, try to resolve them as soon as possible. Bringing your delinquent accounts current will help improve your credit score, and paying off collections may help your score depending on which credit scoring model is used.
Since most negative information like late payments remains on your credit report for seven years, it’s important to start repairing your credit history as soon as possible.
If you have trouble with credit card debt, consider talking to a credit counselor to create a debt management plan. They may be able to negotiate lower monthly payments and interest with your creditors and help you pay off old collection accounts faster. Some may even work to get these negative marks removed from your report.
7. Get a Secured Credit Card
If you are just starting out or have had credit problems in the past, applying for a secured card can help you improve your credit score. When you apply for a secured card, you make a security deposit that the issuer will use as collateral if you are unable to pay.
Monthly payments on a secured credit card will help build your credit score. You should look for secured cards that report to all three major credit bureaus in order to take advantage of the credit-building benefits of credit cards.
The Dollar Differences in Credit Score Ranges
The difference between good credit and bad credit can add up to thousands of dollars of interest over your lifetime.
The higher your credit score range, the less risk you pose to lenders and the more likely you are to be approved for a loan with a lower interest rate.
For this reason, having a good credit score can save you thousands of dollars in interest costs.
However, those with low credit scores will have trouble getting approved for a loan, and those who do may be required to pay a higher interest rate to offset the increased risk of lending. Therefore, having a low credit score means you pay more for financing big-ticket items like a car or a home.
Why You Should Share What You Learned About a Credit Score’s Range
Sharing your knowledge about credit score ranges will help people understand the importance of maintaining a good credit score. To get financing for big-ticket items or a dream home, your credit score must reflect your financial responsibility. In the long run, consumers will save money and have easier access to credit when they have a history of good credit habits.
For lenders to feel confident that you are financially responsible, you should maintain a good credit mix of accounts including a checking account, savings account, and an investment portfolio.
Follow the credit tips above, such as maintaining a low credit utilization rate, making on-time payments, and not opening too many accounts at one time so that you can maintain a good credit score.
Conclusions on Credit Score Ranges
It’s important to understand credit score ranges and realize that they are a reflection of your creditworthiness.
Positive credit habits can open doors to financial opportunities that you would not be able to access otherwise, so start building up your credit history and credit scores now. Finally, make sure to keep up your good credit habits consistently to set yourself up for financial success in the future.
Read more: tradelinesupply.com




 A credit score is a three-digit number that can greatly impact your life.
A credit score is a three-digit number that can greatly impact your life. 











 When it comes to credit scores, there’s a lot of confusion and misinformation out there. Our credit scores impact our lives in more ways than you might think, yet, unfortunately, they are complicated and difficult to understand. In this article, we’ll clear up what credit scores are, why they matter, how to build credit, and how to improve your credit score.
When it comes to credit scores, there’s a lot of confusion and misinformation out there. Our credit scores impact our lives in more ways than you might think, yet, unfortunately, they are complicated and difficult to understand. In this article, we’ll clear up what credit scores are, why they matter, how to build credit, and how to improve your credit score.