Ask an Expert: How Do I Build Good Credit From Scratch?
The NFCC often receives readers questions asking us what they should do in their money situation. We pick some to share that others could be asking themselves and hope to help many in sharing these answers. If you have a question, please submit it on our Ask an Expert page here.
This week’s question: I need some advice in regards to my credit report and good ways that I can begin to build up my credit. I have no credit at all. Eventually within five years once I’m out of school I want to buy a house.
Building credit from scratch will take some time and effort, just like getting a job after graduating from school. You can think about good credit as a means to an end: you need good credit to finance big purchases and get the best interest rates and repayment terms on loans and mortgages. So, getting your credit ready is an excellent start to buying a home in the near future.
What is on Your Credit Report?
Your credit is a record of your monthly financial credit transactions. Your creditors report your activity to the three credit bureaus, Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion, and they use that data to generate a credit score. Your credit report also includes your personally identifying information such as your name, addresses, social security, and some public records such as bankruptcies and judgments and tax liens, if you have any. To start generating data for your credit report, you need to get a credit line. The easiest way to do that is to get a secured credit card. Many banking institutions issue secured credit cards, and they work pretty much like a regular credit card. The main difference is that these cards are backed by a cash deposit, which usually corresponds to the card’s credit limit.
Be Strategic
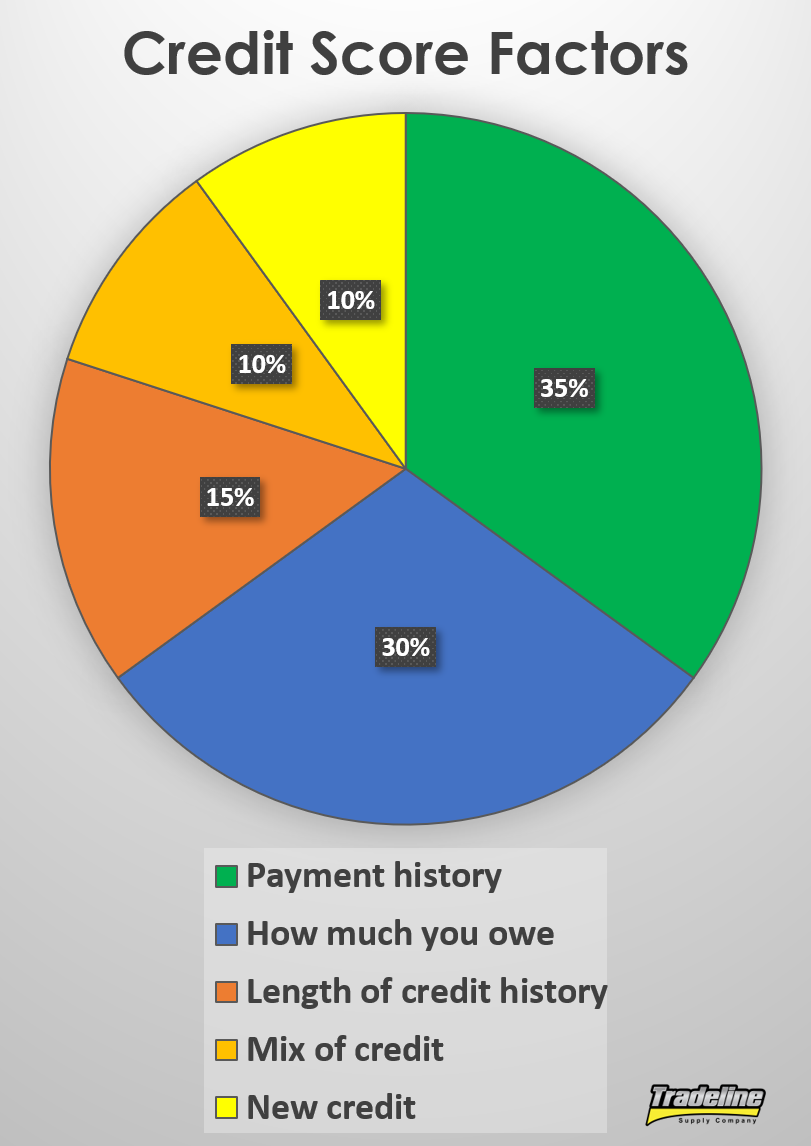
Learning how to use your credit card strategically is equally as important as getting that credit line. Your credit score takes into consideration several factors. The factor that influences your score the most is whether you pay your accounts on time and as agreed. Late or insufficient payments are very detrimental to your credit history. So, you should plan to pay in full and before your due date. Another important factor is your utilization ratio, which is how much you owe compared to your available credit. To have a balanced ratio, experts recommend that you use only 30% or less of your available credit in every billing cycle. For instance, if you have a $500 credit limit, you should be using less than $150.
Yet another factor is the age of your credit history. The older your credit history, the more history and data you’ll have to establish a solid credit history. Achieving this will just require time and your continued effort. The other two factors to keep in mind are the mix of credit you have (credit cards and loans) and how often you ask for new credit. Too many new credit inquiries reflect negatively on your score, so it’s important that you only apply for new credit sporadically. In your case, you should keep your secured credit card for at least a year before applying for a regular credit card. In some cases, your creditor may even upgrade your secured credit card to a regular one and return your cash deposit.
It’s never too soon to start building your credit. And once you learn healthy credit management habits, it will be very easy for you to manage your credit and use your credit cards responsibly on a daily basis. If you feel you need additional guidance or personalized help to get you started, you can always reach out to an NFCC Certified Financial Counselor. They are ready to help over the phone, online, and in-person if it’s available in your state. Good luck!
The post Ask an Expert: How Do I Build Good Credit From Scratch? appeared first on NFCC.
Read more: nfcc.org